Unraveling the VW 1.8T Engine: Efficiency vs Performance

Volkswagen’s journey in making engines has been like a road trip filled with exciting stops. From the old days when cars were air-cooled to the modern days of powerful engines, Volkswagen has been on a quest to improve engines.
One important stop on this journey is the creation of the famous VW 1.8T engine. This engine is like a superhero—it’s robust, efficient, and best of all addictive.
The VW 1.8T Engine’s Birth
The introduction of the VW 1.8T engine was a turning point in Volkswagen’s plan for fast and powerful cars. They introduced “forced induction” to make their cars really fast.
Turbochargers were introduced and together with “direct injection” made the VWs from this era potent but still fuel efficient.
The VW 1.8T engine was like a magic potion. Fans loved it for both power and good fuel mileage.
VW 1.8T Engine - First Generation
Volkswagen introduced the first version of the VW 1.8T engine in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
This was a time of change for cars, and this engine was like a trailblazer. It showed that you could have both power and not consume gallons of fuel.
VW 1.8T Engine 1st Gen. features
The defining feature of the first-generation 1.8 T engine was its turbocharger. This technology allowed the engine to deliver impressive power outputs while maintaining a relatively compact size.
This generation introduced direct fuel injection to the 1.8 T engine, an innovation that enhanced the accuracy of fuel delivery for better combustion, resulting in improved power output
The 1.8 T engine’s design emphasized torque delivery across various engine speeds. This characteristic provided drivers with swift acceleration and responsive performance, making it suitable for both city driving and highway cruising.
Despite its power, the first-generation 1.8 T engine managed to strike a balance between performance and fuel efficiency.
The turbocharged technology enabled the engine to generate impressive horsepower while still delivering decent fuel economy, a feat that catered to drivers seeking spirited driving experiences without frequent trips to the pump.
The engine’s compact design made it adaptable to various vehicle platforms. Its small size allowed for versatile installation in different Volkswagen models, contributing to the engine’s widespread use across the brand’s lineup.
Volkswagen’s engineers incorporated cutting-edge materials and manufacturing techniques into the first-generation 1.8 T engine. This led to improved durability, reduced friction, and enhanced overall efficiency, ensuring a long-lasting and reliable powertrain.
With the first-generation 1.8 T engine, Volkswagen successfully demonstrated that performance need not come at the expense of efficiency. The engine’s ability to seamlessly blend power and economy marked a turning point in the industry, influencing the development of subsequent generations.
VW 1.8T Engine - Second Generation
As time went on, the VW 1.8T engine got even better. From the early 2000s to the mid-2010s, the second version came out. This was like a new chapter in the engine’s story. It was like the engine was growing up and getting better.
VW 1.8T Engine 2nd Gen. features
The second-generation 1.8 T engine retained the turbocharging technology that defined its predecessor but introduced refinements to optimize its performance. With improved turbocharger design and management systems, this engine delivered even more responsive power delivery and reduced turbo lag.
Building upon the success of the first generation, the second-generation 1.8 T engine further refined its direct injection technology.
With advancements in engine management systems and turbocharging, the second-generation 1.8 T engine offered higher power outputs compared to its predecessor.
The engine’s design continued to prioritize a broad torque curve, ensuring that power was available across a wide range of engine speeds.
The second generation incorporated enhanced cooling systems to manage the increased heat generated by the improved turbocharger. This improvement contributed to the engine’s overall reliability and longevity, addressing some of the cooling-related concerns from the first generation.
The engine’s electronic control unit (ECU) was refined to allow for more adaptive engine management. This adaptation enabled the engine to adjust parameters based on driving conditions, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and responsiveness in various scenarios.
Just like its predecessor, the second-generation 1.8 T engine continued to be popular among enthusiasts for its modularity. Aftermarket tuning and performance upgrades were readily available, offering drivers the opportunity to push their engine’s performance to even greater heights.
VW 1.8T Engine - Third Generation
The third generation of the VW 1.8 T engine, spanning from the mid-2010s to the present day, exemplified the brand’s pursuit of striking the perfect balance between power, efficiency, and innovation.
Introduced in 2014, this iteration built upon the successes of its predecessors.
VW 1.8T Engine 3rd Gen. features
The third-generation 1.8 T engine embraced advancements in turbocharging technology to deliver even more refined power delivery. With sophisticated variable geometry turbochargers, the engine achieved an ideal balance between low-end torque and high-end power, catering to a wide range of driving scenarios.
Building upon the direct injection technology of previous generations, the third-generation 1.8 T engine integrated improved fuel atomization and injection timing. This enhancement further optimized combustion efficiency, contributing to increased power output and reduced emissions.
To enhance fuel efficiency without compromising performance, the third generation introduced cylinder deactivation technology. During low-load conditions, the engine could deactivate specific cylinders, effectively reducing fuel consumption while maintaining a seamless driving experience.
The engine’s design continued to prioritize a broad and accessible torque band, ensuring responsive acceleration throughout the rev range.
The third-generation 1.8 T engine featured an advanced engine management system that employed real-time data to optimize performance. This system adapted to driving conditions and driver behavior, ensuring a dynamic and engaging driving experience while still maintaining efficiency.
The third generation embraced lightweight materials and improved construction techniques to enhance overall engine efficiency. These innovations not only contributed to better fuel economy but also reduced friction and improved engine longevity.
The engine’s cooling and heat management systems were further refined to manage the increased thermal demands brought about by advanced turbocharging and combustion technologies.
The engine’s electronic systems were designed to integrate seamlessly with the vehicle’s driver assistance and connectivity technologies. This integration allowed for improved responsiveness, adaptability, and overall driving experience.
Common problems with the VW 1.8T engine
Despite their impressive performance and efficiency, the VW 1.8 T engine generations have been subject to certain common issues reported by users over the years.
Here are some of the common issues reported across different VW 1.8 T engine generations:
Oil sludge buildup: This issue has been reported in some earlier generations of the 1.8 T engine. Oil sludge can accumulate over time due to factors like inadequate maintenance or using low-quality oil. This buildup can clog oil passages, leading to reduced lubrication and potential engine damage.
Ignition coil failures: Across various generations, issues with ignition coils have been reported. Faulty ignition coils can lead to misfires, rough idling, and a decrease in overall engine performance.
Timing belt or chain problems: In some cases, timing belts or chains may fail, causing significant engine damage.
Cooling system concerns: Overheating can occur due to cooling system malfunctions, such as failing water pumps, thermostats, or radiator issues.
Turbocharger failures: While the 1.8 T engine’s turbochargers enhance performance, they can also experience wear and tear over time. Issues like turbocharger shaft play or bearing failure can result in reduced boost pressure, decreased power, and increased exhaust smoke.
Carbon deposits on intake valves: In engines with direct injection, carbon deposits can accumulate on intake valves due to the absence of fuel washing over them. This can lead to decreased airflow, reduced engine efficiency, and potential drivability issues.
PCV system failures: Problems with the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system can lead to oil leaks, increased oil consumption, and compromised engine performance.
Fuel injector issues: Fuel injectors can become clogged or develop leaks, resulting in uneven fuel distribution and poor engine performance.
Emission control component failures: With increasingly stringent emission standards, failures in emission control components like catalytic converters or oxygen sensors can lead to reduced engine performance and increased emissions.
Some owners have reported higher-than-expected oil consumption in certain generations of the 1.8 T engine.
VW 1.8T engine Tuning Potential
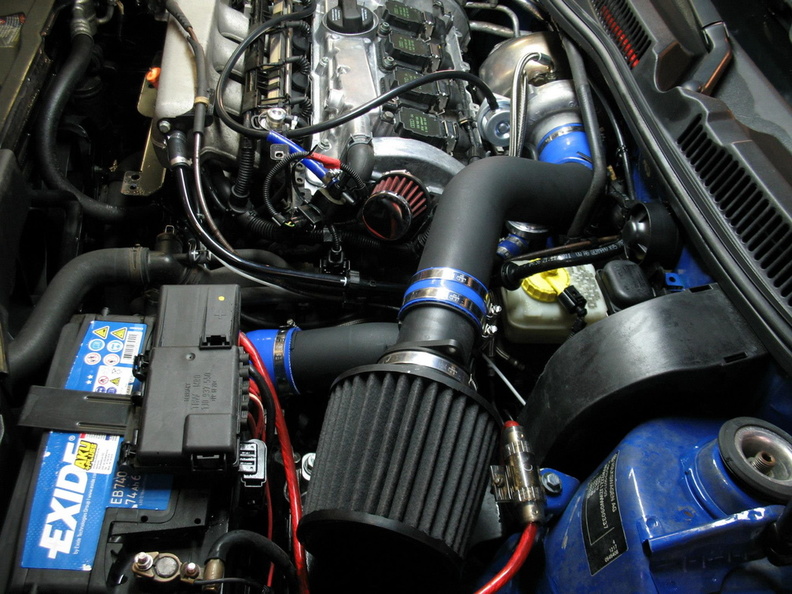

The VW 1.8 T engine has captured the attention of car enthusiasts and tuners around the world due to its inherent potential for performance upgrades.
The modular design and robust engineering of the engine make it an ideal candidate for tuning, allowing owners to unlock even greater power and driving dynamics.
Here’s a closer look at VW 1.8 T engine tuning:
- One of the most common ways to enhance the performance of the 1.8 T engine is through electronic control unit (ECU) remapping. By adjusting the engine’s parameters, such as fuel injection timing, turbocharger boost levels, and ignition timing, tuners can optimize the engine’s performance for improved power and torque output.
- Upgrading the turbocharger or even installing a larger one can significantly increase the engine’s power potential. Aftermarket turbochargers can provide higher boost levels, quicker spooling, and more efficient airflow, resulting in enhanced overall performance.
- Installing a high-flow aftermarket intake system and exhaust components can improve air intake and exhaust flow. This can lead to increased horsepower, quicker throttle response, and a more aggressive engine note.
- Upgrading the intercooler can help reduce intake air temperatures, which is crucial for maintaining consistent performance, especially under demanding driving conditions. A more efficient intercooler can lead to better power delivery and reduced heat-related performance loss.
- For those seeking extreme levels of performance, upgrading to forged internals such as pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts can handle higher power outputs and increased stress from forced induction setups.
- Increasing power often requires more fuel to be delivered to the engine. Upgrading the fuel injectors, fuel pump, and fuel lines ensures proper fuel supply to accommodate the engine’s increased demands.
- Performance tuning is not just about engine modifications; enhancing suspension components and upgrading braking systems can help translate the increased power into improved handling and stopping capabilities.
- After making modifications, dyno tuning is essential to fine-tune the engine’s parameters for optimal performance. This process involves testing the engine on a dynamometer to adjust fuel, timing, and other parameters to achieve the best power and torque output.
- It’s important to strike a balance between performance gains and engine reliability. Pushing the engine to its limits without proper supporting modifications can lead to premature wear, increased stress, and potential failures.
While there are DIY tuning solutions available, seeking the expertise of professional tuners is recommended for optimal results. They have the knowledge and experience to create a custom tuning strategy that maximizes performance while maintaining engine health.
cars that use the VW 1.8T engine
Some of the cars that have utilized the VW 1.8T engine include:
Volkswagen Golf/GTI
Volkswagen Jetta
Volkswagen Passat
Also related articles ..
VW VR6 engine reliability
Explore the VW VR6 Engine Reliability and discover key insights to understand the true reliability of this rig.

EA888 Engine Reliability
Get all the details you need on the EA888 Engine Reliability Volkswagen TSI engine