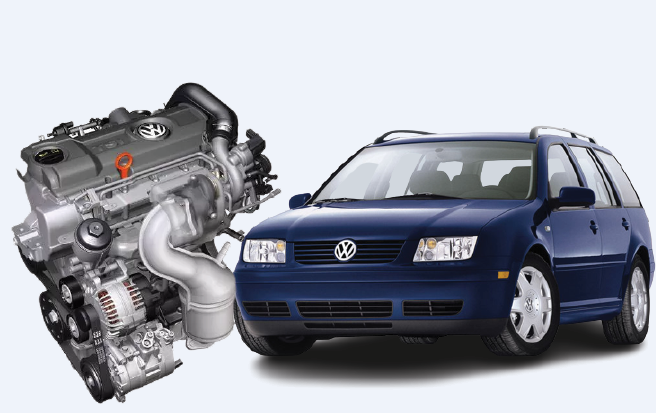
EA888 Engine Reliability: A Powerhouse or a miss?

The EA888 engine is a gasoline engine made by Volkswagen Group. It started in 2004 and has seen many improvements over the years.
Let’s look at the generations of the EA888.
EA888 Engine Reliability - 1st Generation
Introduced in the mid-2000s, the 1st Generation EA888 engine a four-cylinder, turbocharged, direct-injection gasoline engine was a great piece of art.
It was released in 2008 and has been widely used in various Volkswagen vehicles. The EA888 engine family includes several different versions with various displacements and power outputs.
The 1st Gen. EA888 engines were known for their efficient performance, good fuel economy, and low emissions. They have been used in a wide range of vehicles, from compact cars to SUVs and performance models. Some of the notable vehicles that used the 1st Generation EA888 engine include:
Volkswagen Golf Mk6 GTI: The popular hot hatch featured the 2.0-liter EA888 engine with different power outputs in different markets.
Volkswagen Passat B6: The midsize sedan was available with the EA888 engine in certain markets.
EA888 Engine Reliability - 2nd Generation
The second generation improved on its predecessor, with more power and precision. They made the engineering better, improved turbocharging, and fuel delivery, making it popular among performance enthusiasts.
Some key features of the 2nd Generation EA888 engines include:
- Turbocharging
- Direct Fuel Injection
- Variable Valve Timing
- Modular Design: Volkswagen designed these engines to be modular, meaning they share many common components and technologies, which streamlines production and reduces manufacturing costs.
- Displacement: The 2nd Generation EA888 engines typically come in various displacements, ranging from 1.8 to 2.0 liters.
Continuous improvements like the redesigned pistons and rings and improved cylinder walls. Volkswagen also introduced a variable oil pump for better performance.
EA888 Engine Reliability - 3rd Generation
In the third generation, they made the cylinder walls thinner and improved the pistons, rings, and crankshaft for efficiency and reliability. They introduced direct fuel injection and other technology, making it more reliable and efficient.
The aluminum head design was smart, and they solved the carbon deposit issue with a dual-injector setup.
Volkswagen made performance variants with enlarged exhaust valves, a stronger intake cam, and a powerful turbo.
The EA888 engines were designed in various displacements, typically ranging from 1.8 to 2.0 liters.
EA888 Engine Reliability - 4th Generation
The latest generation, the fourth, took reliability and performance to new heights with more engineering improvements, advanced turbocharging, and optimized combustion.
The EA888 engine has come a long way and is now known for its reliability. But let’s look at some common problems for a better understanding.
Some of the notable features added to the EA888 engines in the 4th generation include:
- Twin-scroll Turbocharger
- Cylinder Deactivation (COD): During light-load driving conditions, the engine can deactivate two of its four cylinders, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
- In certain iterations of the EA888 engines, the exhaust manifold is integrated into the cylinder head. This design reduces weight, improves thermal efficiency, and allows for more precise temperature control.
- Dual Injection System – This setup optimizes fuel delivery for different driving conditions, leading to improved fuel economy and performance.
- Some variants of the EA888 engines feature an active cooling system that can vary the coolant flow to different engine components as needed, improving efficiency and reducing warm-up times.
- The direct injection system in EA888 engines employs a high-pressure fuel rail to deliver fuel to the injectors with precision
- The EA888 engines often feature variable valve timing and lift, allowing the camshafts to adjust their timing and lift profiles based on engine speed and load, optimizing performance and efficiency.
The engines have an optimized air intake system that enhances airflow into the engine, promoting efficient combustion and improved performance.
EA888 Engine Reliability - Common Problems and Solutions
The EA888 engine, when not well-maintained, can face a common problem with its timing chain stretching. This issue is often caused by worn timing tensioners in other engines.
Another challenge is excessive oil consumption, which was seen in some older versions of the EA888 engine. The problem can be due to worn piston rings, valve stem seals, or PCV system issues. Proper maintenance and care can help reduce the risk of oil leaks.
To keep the engine in good condition, it’s recommended to change the engine oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on the driving conditions and the engine model.
Three components that frequently fail in EA888 engines are the Water Pump, PCV system, and High-Pressure Fuel Pump.
Water Pump Failure: Causes, Signs & Solutions
The water pump in the EA888 engine plays a vital role in keeping the engine cool by circulating coolant throughout the system. When it fails your engine could present an array of issues.
Causes of Water Pump Failure
As the engine accumulates mileage, the water pump’s bearings, seals, and impeller can wear out, leading to reduced performance and eventual failure.
Contaminated coolant, either due to the presence of debris or inadequate maintenance, can accelerate the wear and deterioration of the water pump.
Continuous engine overheating can put significant strain on the water pump, causing it to fail prematurely.
Incorrect installation of the water pump or using low-quality replacement parts can contribute to its failure.
Signs of Water Pump Failure
One of the most common signs of water pump failure is the presence of coolant leaks around the pump or near the front of the engine.
An overheating engine could be a result of a malfunctioning water pump that isn’t circulating coolant well.
A worn-out water pump can cause the pulley to wobble or make noise, indicating a problem with the pump’s bearings.
A grinding or whining noise, especially when the engine is running indicates a water pump on the way out.
If the water pump is not circulating coolant effectively, steam may be visible coming from the engine bay.
Solutions for Water Pump Failure
If the water pump is confirmed to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new OEM or high-quality aftermarket pump.
Flushing the cooling system and refilling it with fresh coolant can help prevent contamination and extend the life of the new water pump.
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including inspecting the cooling system, can help detect potential issues with the water pump early.
Using the right type and quality of coolant recommended by the manufacturer can contribute to the water pump’s longevity.
Ensure the water pump is installed correctly by following the manufacturer’s guidelines or seeking professional installation.
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System Issues
The PCV system is responsible for regulating crankcase pressure to maintain engine efficiency. When it fails, various problems can arise.
To prevent PCV system issues, regular inspection and maintenance are necessary. If any problems are detected, the PCV system should be promptly repaired or replaced to ensure the engine’s proper functioning.
Understanding these common issues and implementing proper maintenance can help ensure the longevity and reliability of the EA888 engine.
Causes and symptoms of PCV valve failure
The PCV valve can experience failure due to several reasons:
Clogging: Over time, carbon deposits and sludge can clog the PCV valve, blocking airflow and causing it to malfunction.
Wear and tear: As the engine accumulates mileage, the PCV valve may wear out, leading to failure.
Excessive blow-by: When the engine produces more blow-by gases than the PCV system can handle, it strains the valve and can cause failure.
Poor Maintenance: Neglecting regular engine maintenance, like oil changes and air filter replacements, can contribute to PCV valve failure.
Symptoms of a failing PCV valve include:
Increased Oil Consumption: A failing PCV valve can allow excessive oil vapors to escape from the crankcase, leading to more oil consumption.
Poor Engine Performance: Improper regulation of crankcase pressure can result in reduced power and acceleration.
Rough Idling or Stalling: A malfunctioning PCV valve can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to rough idling or stalling at low speeds.
Check Engine Light: In some cases, a faulty PCV valve can trigger the check engine light on the dashboard, indicating an emissions system problem.
Excessive Exhaust Smoke: If the PCV valve is stuck open, it can draw oil vapors into the intake manifold, causing excessive smoke from the exhaust.
Engine Misfires: An imbalanced air-fuel mixture due to PCV valve failure can lead to engine misfires and overall performance issues.
To address PCV valve failure:
Regularly inspect and clean the PCV valve during routine maintenance to remove carbon deposits.
Replace the PCV valve with a new OEM or high-quality aftermarket valve if it is damaged or malfunctioning.
Address underlying engine problems causing excessive blow-by gases, such as replacing worn piston rings.
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, including timely oil changes and air filter replacements.
Use high-quality engine oil that meets the manufacturer’s specifications to reduce carbon deposit formation and prolong the PCV valve’s life.
High-Pressure Fuel Pump (HPFP) Failure : Causes and Symptoms
HPFP failure can be caused by the following factors:
Contaminated Fuel: Impurities and debris in the fuel can damage the internal components of the HPFP, leading to reduced efficiency and eventual failure.
Poor Lubrication: The HPFP relies on fuel for lubrication of its moving parts. Running the engine with a low fuel level for extended periods can lead to inadequate lubrication and premature wear of the pump.
High Operating Temperatures: Excessive heat can cause the HPFP to overheat, reducing its performance and eventually causing failure.
Symptoms of HPFP Failure include:
Loss of Power: A failing HPFP may not deliver the required fuel pressure to the engine, resulting in reduced power and slower acceleration.
Rough Idling: The HPFP’s struggle to maintain consistent fuel pressure can lead to rough idling or stalling when the engine is at a standstill.
Engine Misfires: Inadequate fuel pressure can cause misfires, leading to rough engine performance and potential check engine light activation.
Increased Fuel Consumption: A failing HPFP may not efficiently deliver fuel to the engine, causing increased fuel consumption and reduced overall efficiency.
Hard Starting: Difficulty starting the engine, especially after it has been sitting for a while, can be a sign of HPFP failure.
Engine Warning Light: A failing HPFP can trigger the engine warning light on the dashboard, indicating the need for immediate attention.
To address HPFP failure:
Regularly clean the fuel system and use high-quality fuel additives to prevent contamination and maintain smooth operation.
Change the fuel filter at recommended intervals to maintain fuel quality and prevent debris from reaching the HPFP.
Always use high-quality fuel from reputable sources to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure optimal engine performance.
EA888 Tuning Potential

Upgrading the EA888 engine with aftermarket modifications can boost its performance, but it’s essential to choose wisely and ensure professional installation to maintain reliability.
For Gen 1 and Gen 2 engines, carbon buildup can be a concern. To prevent this, using high-quality gasoline, performing regular intake valve cleanings, and using fuel additives designed to reduce carbon deposits are recommended.
For a stage 1 or 2 tune, the engine block can handle upgrades like forged pistons, drop forged connecting rods, and a forged crankshaft. The block itself, made of cast iron, is robust and can accommodate these enhancements.
The IS38 Turbo is a top recommendation to support the extra power, which can exceed 400bhp.
With proper care and regular maintenance, the EA888 engine is designed to deliver reliable performance for an extended period. Taking good care of the engine will ensure it remains a fantastic rig.
cars that use the EA888 engine
Some of the cars that use the EA888 engine include:
- Volkswagen Golf GTI and Golf R
- Volkswagen Passat and Arteon:
- Volkswagen Tiguan and Tiguan R
- Volkswagen Jetta GLI
Top picks ..
VW VR6 engine reliability
Explore the VW VR6 Engine Reliability and discover key insights to understand the true reliability of this rig.
Plus more articles