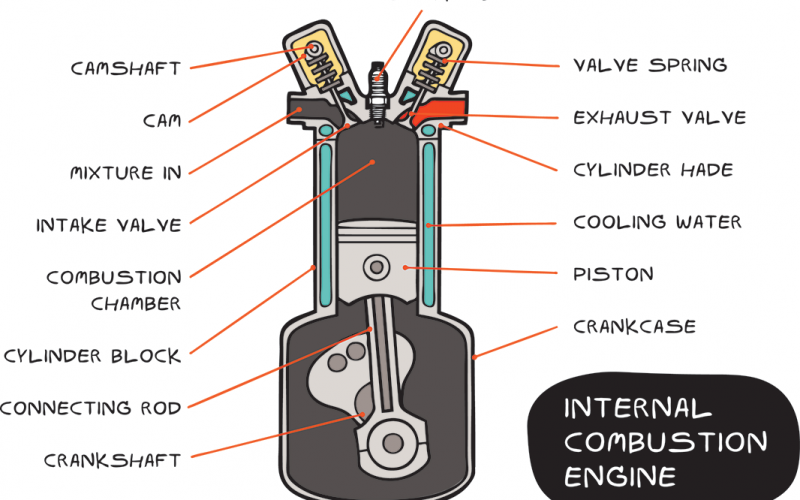
19 most common engine terms and their simplified meaning
Let’s understand engine terms and simplify the jargon together…
Understanding how your engine works and functions are important in the event you have to identify and solve car problems. In case you have been overwhelmed with a ton of information on engine parts and jargon, you have come to the right place.
Despite the title here we won’t limit ourselves exclusively to the engine but we could include terms associated with closely related car parts.
Feel free to skip to terms you might not be familiar with…
By now you must be aware of internal combustion and external combustion engines, incase you don’t we did this article on engine classifications.
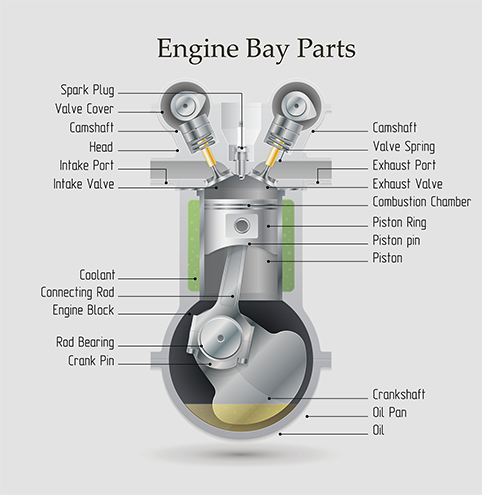
engine terms - Engine bay parts names
The cylinder block also referred to as the engine block – Holds the cylinders where combustion occurs and can accommodate between 1 and 16 cylinders. The block is made of aluminum in newer vehicles or iron for heavy-duty and aged engines. Besides the cylinders, the motor block houses the rotating components of the engine and acts as the pathway for oil and coolant fluids that are vital to an engine’s core operation.
- Cylinder head – this encloses the cylinder and controls the movement of air into the cylinder for compression mixed with fuel.
- Piston – located at the bottom of the cylinder, it creates motion as a result of upward and downward movement. As it moves up it compresses the air and fuel mix which results in an explosion that sends it back down again to turn the crankshaft. The two parts – piston and crankshaft are connected via a rod
- Compression – Used to measure the capacity of an engine to squeeze the air and fuel in the cylinder. The more compression, the more power you get from a combustion cycle.
- Crankshaft – One of the most important parts of an internal combustion engine. As we just discussed, the crankshaft is turned by the piston’s downward motion. The crankshaft is connected to a drivetrain. The drive train helps move the wheels.
- Camshaft – Not to be confused with the crankshaft, the camshaft helps the engine time the opening and closing of the valves that let in the air into the cylinder for combustion. Timed to synchronize with the crankshaft.
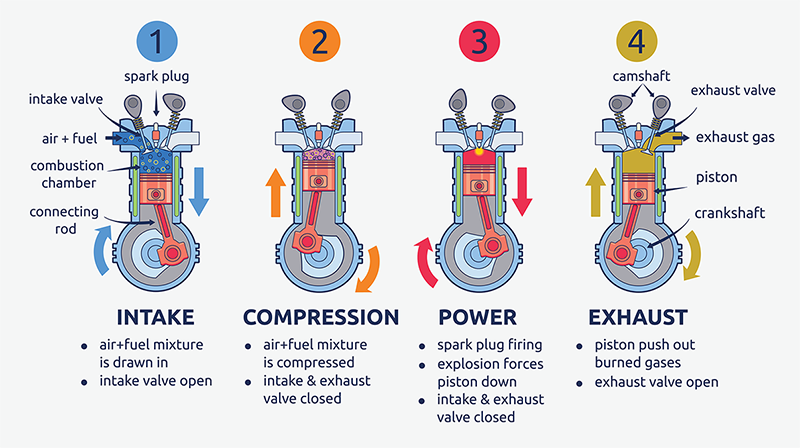
common engine parts as they appear for each stage
6. Oil pump – supplies oil to the moving engine parts. Oil pumps are prone to tear and wear as a result of picking contaminants during the combustion process. Therefore they must be replaced often as instructed by the manufacturer.
7. Timing and accessory belts – You probably have heard about a timing belt…or maybe not. It is responsible for keeping the crankshaft and camshaft in sync hence the term timing. Sometimes gears and a chain are used to play the timing belt role. The alternator and AC compressor also rely on a different accessory belt. Timing belts and chains are also prone to tear and wear and thus need maintenance or replacement.
8. Alternator – generates power when the engine is running. The alternator is driven by a belt and the power generated runs the electrical components in the car and most importantly, charges the car battery.
9. Displacement – Used to measure the volume inside cylinders which is related to the amount of fuel and air that the cylinders can hold before compression takes place.
10. Drive train: The drive train is responsible for delivering power from the engine to the wheels and consists of the clutch, transmission, driveshaft, differential, and the axle on which the drive wheels are situated.
11. Engine flywheel: A spinning plate that helps engage the clutch disk and is found at the end of the crankshaft on vehicles with manual transmissions.
12. Firing order: Depending on the number of cylinders in an engine there is an order that dictates the sequence in which the cylinders fire. It is closely related to the cylinder sequence which refers to the arrangement from the first to the last cylinder. The firing order helps to distribute combustion and reduce engine vibrations.
13. Oil pump – supplies oil to the moving engine parts. Oil pumps are prone to tear and wear as a result of picking contaminants during the combustion process. Therefore they must be replaced often as instructed by the manufacturer.
14. Timing and accessory belts – It is responsible for keeping the crankshaft and camshaft in sync hence the term timing. Sometimes gears and a chain are used to play the timing belt role. The alternator and AC compressor also rely on a different accessory belt. Timing belts and chains are also prone to tear and wear and thus need maintenance or replacement.
15. Alternator – generates power when the engine is running. The alternator is driven by a belt and the power generated runs the electrical components in the car and most importantly, charges the car battery.
16. Displacement – Used to measure the volume inside cylinders which is related to the amount of fuel and air that the cylinders can hold before compression takes place.
17. Drive train: The drive train is responsible for delivering power from the engine to the wheels and consists of the clutch, transmission, driveshaft, differential, and the axle on which the drive wheels are situated.
18. Engine flywheel: A spinning plate that helps engage the clutch disk and is found at the end of the crankshaft on vehicles with manual transmissions.
19. Firing order: Depending on the number of cylinders in an engine there is an order that dictates the sequence in which the cylinders fire. It is closely related to the cylinder sequence which refers to the arrangement from the first to the last cylinder. The firing order helps to distribute combustion and reduce engine vibrations.
Conclusion
Armed with the understanding of engine terms and definitions you can confidently take care of your car or comprehend what your mechanic is talking about.
This list keeps developing because a car engine has more than the parts listed here. We’ll curate and pick the most common and confusing car engine jargon.
